State Details
Parameters:
Maximum Inventory (
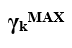 ):
): Material Price (
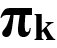 ):
):
| Time | Amount | |
|---|---|---|
Task Details
Parameters:
Processing Cost (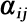 ) )
| Processing Time (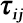 ) )
| |
|---|---|---|
| {{pair.unit.displayName}} | ||
| You have not associated any units to this task. | ||
Unit Details
Unit: {{unit.displayName}}
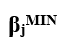 ):
): 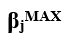 ):
): Associate tasks with this unit:
{{task.displayName}}Connection Details
Fraction of materialtask {{connection.from.displayName}} consumedproduced by taskmaterial {{connection.to.displayName}} (
 ):
): | {{connection.getFractionDisplaySign()}} |
Choose Objective Function
Choose Solution Methods (Optional)
*Privacy Policy
The email address is required to provide the results to the user. The email addresses are not stored locally and sent to NEOS server, which requires the same to communicate the results to the user. Please refer to NEOS Terms of Use.
Timestamp: {{convertTime(runtimeResult.Timestamp)}}
- Objective Value: {{runtimeResult.selectedModel.ObjectiveValue}}
- Objective Value based on DCA: {{runtimeResult.DCAObjectiveValue}}
- Relaxed Objective Value: {{runtimeResult.selectedModel.RelaxedObjectiveValue}}
- Runtime: {{runtimeResult.selectedModel.RunTime}}
- Number of Constraints: {{runtimeResult.selectedModel.NumberOfConstraints}}
- Tightening Constraints (Demand Propagation) Included: {{runtimeResult.AnalysisConstraintsOptions.constraints.additionalConstraints.selected}}
- Reformulation Included: {{runtimeResult.AnalysisConstraintsOptions.constraints.reformulation.selected}}
- DCA Used: {{runtimeResult.DCAObjectiveValue != null}}
Help
Instructions:
To create the states select Create Network >> Add State. Once the required states are created, click on Create Network >> Add Task. In the perimeter of each state and task block there are connecting dots which can be dragged and joined to establish connecting arcs between states and tasks.
To add units click on Create Network >> Add Unit. To enter unit capacities and task-unit associations click on the respective units on the Unit Details page. The details regarding the states and tasks can be added by double-clicking on the respective blocks. In the State Details page, storage capacities and material price need to be specified. Initial inventories, material deliveries, and demands can be provided through the Add Delivery/Demand button.
Intermediate demands/deliveries should be entered with the appropriate timing information. For end of the horizon demands, the horizon duration should be defined along with the demand quantities. Demand quantities should be entered as negative numbers, whereas intermediate deliveries should be given as positive numbers. The fraction of material 𝘬 produced (> 0) or consumed (< 0) by task 𝑖 can be entered by double-clicking the connecting arcs.
Once all the relevant information and parameters are entered, the user should go to the Submit Network tab where all the information is consolidated in an input string which the user should save if they want to run the same network again by just pasting the string in the ‘Input String’ box. To incorporate some change in the network parameters, the user can directly modify the string without creating the network again. Once the network is created and all the information of a particular instance is entered, the user should choose the appropriate objective function from the drop-down menu, enter the time step and horizon, and specify the requisite optimality gap. The user can choose a solution method or a combination of methods to increase the computational efficiency. Finally, the user should provide their email address and click on the ‘Submit Network’ button. Once submitted, the user would see a pop-up window confirming their submission.
Video Tutorial:
Resources:
Tightening Constraints :
1) Velez S, Sundaramoorthy A, Maravelias CT. Valid Inequalities Based on Demand Propagation for Chemical Production Scheduling MIP Models. AIChE J., 59(3), 872-887, 2013.(DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/aic.14021).
Reformulation:
1) Velez S, Maravelias CT. Reformulations and Branching Methods for Mixed-integer Programming Chemical Production Scheduling Models. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 52 (10), 3832-3841, 2013. (DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ie303421h)
Discrete-continuous Algorithm:
1) Lee H, Maravelias CT. Combining the Advantages of Discrete- and Continuous-Time Scheduling Models: Part 1: Framework and Mathematical Formulations. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 176-190, 116, 2018. (DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2017.12.003).
2) Lee H, Maravelias CT. Combining the Advantages of Discrete- and Continuous-time Scheduling Models. Part 2: Systematic Methods for Determining Model Parameters. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 128, 557-573, 2019. (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2018.10.020).